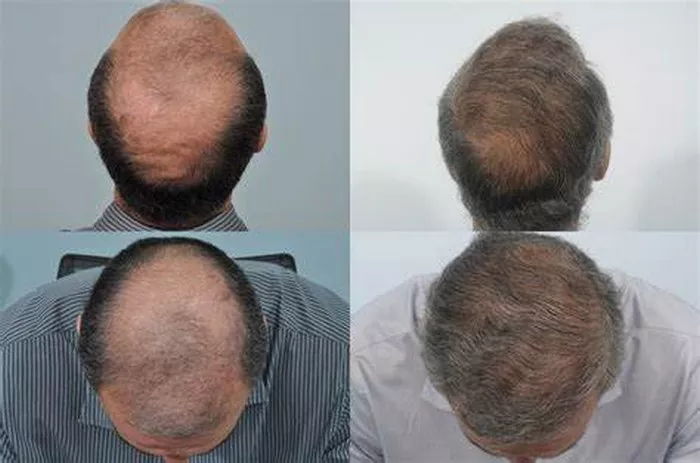
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, impacting their confidence and appearance. Among the various solutions available, hair transplant surgery has become one of the most popular and effective treatments. However, like any medical procedure, it is essential to understand the potential side effects involved before making a decision. In this article, we will explore the common and less common side effects of hair transplant procedures, helping you to make an informed choice about your hair restoration journey.
What Is Hair Transplant Surgery?
Hair transplant surgery involves relocating hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to balding or thinning areas. This process can be performed using different techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). While the procedure is generally safe when performed by qualified surgeons, side effects and risks are inevitable and should be carefully considered.
Common Side Effects of Hair Transplant
1. Swelling and Inflammation
One of the most common side effects after hair transplant surgery is swelling around the forehead and eyes. This swelling usually appears within the first few days after the procedure and gradually subsides within a week. It results from the body’s natural inflammatory response to the trauma caused by hair follicle extraction and implantation.
2. Pain and Discomfort
Although the procedure is done under local anesthesia, patients may experience some pain or discomfort once the anesthesia wears off. This pain is usually mild and manageable with prescribed painkillers. Discomfort can also come from tightness or soreness in the scalp area.
3. Scabbing and Crusting
After the surgery, small scabs or crusts may form around the transplanted hair follicles as the scalp heals. This is a normal part of the recovery process, but improper care can lead to infection or delayed healing. Patients are advised not to pick or scratch the scabs to avoid damaging the grafts.
4. Itching
Itching is another common side effect during the healing phase. It occurs due to the formation of new skin and scabs, as well as mild inflammation. While it can be bothersome, it is important not to scratch the scalp to prevent dislodging grafts and causing infections.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
1. Infection
Though rare, infections can occur after hair transplant surgery if proper hygiene is not maintained. Signs of infection include redness, pus, severe pain, and swelling. Infections require prompt medical treatment, often involving antibiotics, to prevent further complications.
2. Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the inflammation of hair follicles and may occur after surgery. It appears as small pimples or pustules around the transplanted area. This condition can be treated with topical or oral antibiotics but may cause discomfort during recovery.
3. Shock Loss
Shock loss refers to the temporary shedding of existing hair around the transplanted area due to surgical trauma. Although it can be alarming, this hair usually grows back over time. Patients should be reassured that shock loss is often a temporary phenomenon.
4. Numbness or Tingling Sensation
Temporary numbness or tingling can occur around the donor or recipient sites due to nerve irritation during surgery. This sensation usually resolves within a few weeks to months, but in rare cases, it may persist longer.
5. Unnatural Hair Growth or Poor Graft Survival
In some cases, the transplanted hair may grow in an unnatural direction or pattern if the surgeon does not place the grafts carefully. Additionally, some grafts may fail to survive the transplant process, resulting in patchy or uneven hair density.
How to Minimize Side Effects
Choosing a highly experienced and qualified surgeon is the most critical factor in minimizing the risk of side effects. Proper preoperative evaluation and following post-operative care instructions can also significantly reduce complications.
Post-Operative Care Tips
- Keep the scalp clean and follow washing instructions provided by your surgeon.
- Avoid strenuous activities and direct sun exposure for at least a few weeks.
- Take all prescribed medications, including antibiotics and painkillers.
- Avoid scratching or picking at scabs and crusts.
- Attend all follow-up appointments for proper monitoring.
Hair Transplant Recovery: What to Expect
The hair transplant recovery process varies from person to person but generally follows a predictable timeline. In the first week, swelling, redness, and scabbing are common. By the second week, most scabs fall off, and the scalp starts to heal visibly. Shedding of the transplanted hair typically occurs within the first 2 to 4 weeks, followed by new hair growth starting around 3 to 4 months post-surgery. Full results are usually visible after 9 to 12 months.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most side effects are mild and temporary, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe or worsening pain not relieved by medication
- Signs of infection such as fever, pus, or extensive redness
- Persistent numbness or loss of sensation
- Excessive bleeding or unusual swelling
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery offers an effective solution for many suffering from hair loss, but it is essential to understand the possible side effects before proceeding. Most side effects, such as swelling, itching, and mild pain, are temporary and manageable with proper care. However, more serious complications like infection or folliculitis, although rare, should be promptly addressed to avoid lasting damage. By choosing a qualified surgeon and following postoperative instructions diligently, patients can minimize risks and enjoy successful hair restoration results with improved confidence and appearance.
Related Topics:
- Estherian Launches Dedicated DHI Hair Transplant Clinic in Istanbul
- Hair Transplant Industry Booms but Faces Deadly Safety Challenges
- HairSmart Named Top Post-Hair Transplant Shampoo in 2025 Consumer Survey