The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and energy levels. It achieves this by producing hormones called thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence virtually every cell, tissue, and organ in the body. The thyroid gland’s functioning is tightly regulated by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, ensuring that the body’s metabolic processes remain balanced.
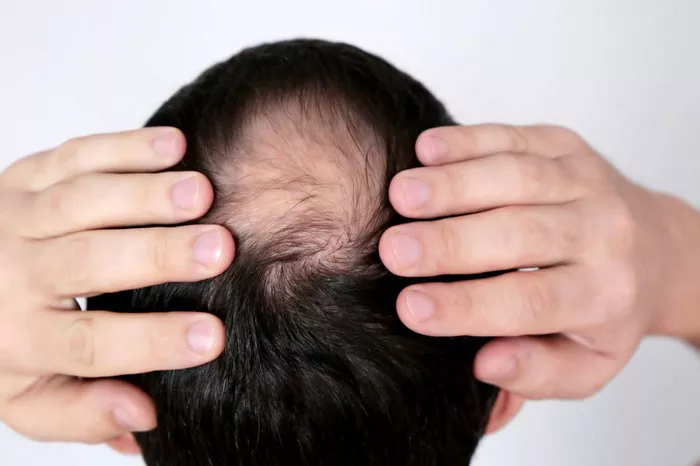
Thyroid conditions encompass a range of disorders that affect the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones, leading to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt numerous bodily functions. One of the common manifestations of thyroid dysfunction is hair loss, which can be distressing for those experiencing it. Understanding the relationship between thyroid conditions and hair loss is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Types of Thyroid Conditions:
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid):
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones, resulting in a slowdown of bodily processes. This condition can be caused by various factors, including autoimmune disorders, iodine deficiency, or thyroid surgery.
Hair loss is a prevalent symptom of hypothyroidism, often characterized by thinning hair and loss of hair density. The hair may become brittle, dry, and prone to breakage, leading to noticeable changes in hair texture. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, is a common cause of hypothyroidism. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the thyroid gland becomes inflamed and progressively loses its ability to produce hormones, resulting in hypothyroidism and associated symptoms like hair loss.
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid):
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones, accelerating metabolic processes throughout the body. This heightened metabolic state can lead to various symptoms, including weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Thinning hair is a characteristic symptom of hyperthyroidism, although it differs from the pattern observed in hypothyroidism. In hyperthyroidism, hair may become fine and silky, and there may be an increased shedding of hair. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones, is a common cause of hyperthyroidism. In Graves’ disease, the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism and its associated symptoms, including hair loss.
How Thyroid Conditions Affect Hair Growth:
Hair growth occurs in a cyclical process consisting of three phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). The thyroid hormones T3 and T4 play a crucial role in regulating the hair growth cycle by influencing the duration of each phase and the activity of hair follicles.
Disruptions in thyroid hormone production can disturb the delicate balance of the hair growth cycle, leading to abnormal hair growth patterns and eventual hair loss. In hypothyroidism, reduced levels of thyroid hormones can prolong the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle, causing more hairs to enter the shedding phase simultaneously. This results in diffuse hair loss and decreased hair density over time.
Similarly, in hyperthyroidism, excess thyroid hormones can accelerate the hair growth cycle, causing hairs to progress rapidly through the growth phase and enter the shedding phase prematurely. This leads to increased hair shedding and a decrease in hair volume and thickness.
In both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, the disrupted hormone levels can also affect the quality of hair follicles, making them more prone to breakage and damage. Additionally, thyroid hormones play a role in regulating the production of sebum, the skin’s natural oil. Imbalances in sebum production can contribute to scalp dryness or oiliness, further exacerbating hair loss.
Other Considerations:
In addition to thyroid-related hair loss, individuals with thyroid conditions may also experience hair loss due to comorbid autoimmune conditions such as alopecia areata. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder characterized by patchy hair loss, often resulting in circular bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. The exact relationship between thyroid conditions and alopecia areata is not fully understood, but both conditions involve dysregulation of the immune system.
Furthermore, certain medications used to treat thyroid conditions, such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism or methimazole for hyperthyroidism, may list hair loss as a potential side effect. While these medications are essential for managing thyroid disorders, individuals experiencing hair loss should discuss their concerns with their healthcare provider to explore alternative treatment options or adjunct therapies.
Symptoms of Thyroid-Related Hair Loss:
Hair loss associated with thyroid conditions typically develops gradually over time and may not be immediately noticeable, especially in the early stages of thyroid dysfunction. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may observe increased hair shedding during routine activities such as washing or brushing their hair.
Unlike hair loss patterns observed in other conditions such as male or female pattern baldness, thyroid-related hair loss tends to be diffuse and uniform, affecting the entire scalp rather than specific areas. This diffuse thinning can be particularly distressing for individuals accustomed to having thick, healthy hair.
It’s essential to recognize that hair loss caused by thyroid conditions is usually temporary and reversible with appropriate treatment and management. Once thyroid hormone levels are restored to normal through medication or other interventions, the hair growth cycle typically resumes its normal rhythm, and lost hair may gradually regrow over time.
Treatment and Management:
Effective management of thyroid conditions is crucial for alleviating symptoms like hair loss and promoting overall health and well-being. Treatment strategies may vary depending on the type and severity of the thyroid disorder but often involve a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and dietary interventions.
For hypothyroidism, the primary treatment involves hormone replacement therapy using synthetic thyroid hormones such as levothyroxine. By restoring thyroid hormone levels to normal, this medication helps alleviate symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss. It’s essential to take thyroid medication as prescribed and undergo regular thyroid function tests to monitor hormone levels and adjust medication dosages as needed.
In cases of hyperthyroidism, treatment options may include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or thyroidectomy (surgical removal of the thyroid gland). These interventions aim to normalize thyroid hormone levels and reduce symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism, including hair loss.
In addition to medication, dietary modifications and supplements may also play a role in managing thyroid-related hair loss. Ensuring an adequate intake of essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, selenium, and biotin is essential for supporting healthy hair growth. Foods rich in these nutrients include lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts.
Furthermore, adopting a balanced and nutritious diet that supports thyroid function can help optimize hormonal balance and promote hair health. Avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats while prioritizing nutrient-dense whole foods can positively impact thyroid function and overall well-being.
It’s important to note that hair growth is a gradual process, and it may take several months for noticeable improvements to occur after initiating thyroid treatment. Patience and consistency with treatment and lifestyle modifications are key to achieving optimal results.
In conclusion, thyroid conditions can significantly impact hair health and contribute to hair loss through disruptions in hormone production and the hair growth cycle. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of thyroid-related hair loss and implementing appropriate treatment and management strategies, individuals can effectively address this symptom and restore hair health and vitality. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring of thyroid function and hair growth progress. With proper care and attention, individuals with thyroid conditions can achieve healthy, vibrant hair and improve their overall quality of life.
FAQs
How do I know if my thyroid is causing hair loss?
Hair loss can be a symptom of thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. If you’re experiencing excessive hair shedding, thinning hair, or bald patches, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform tests to assess your thyroid function, including blood tests measuring levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, and T4) and antibodies.
How does your body feel when you have thyroid problems?
Thyroid issues can manifest in various ways depending on whether the thyroid is overactive or underactive. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold sensitivity, dry skin, and constipation. Conversely, hyperthyroidism may cause symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, sweating, anxiety, and irritability.
What are the symptoms of thyroid problems in females?
In addition to hair loss, women may experience menstrual irregularities, fertility issues, changes in libido, and mood swings due to thyroid dysfunction. Other symptoms include fatigue, weight changes, dry skin, and sensitivity to cold or heat.
How does thyroid hair loss look like?
Thyroid-related hair loss typically presents as diffuse thinning rather than bald patches. You may notice increased shedding when brushing or washing your hair, and your hair may appear sparse overall. In some cases, thinning may be more pronounced at the crown or along the parting line. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.