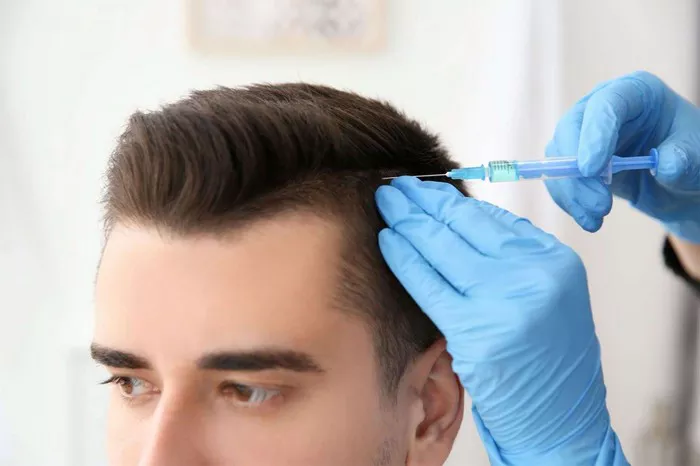
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, both men and women. While there are many topical treatments and medications available, hair transplantation remains the most effective and long-lasting solution for many. However, not everyone is keen on undergoing hair transplant surgery due to concerns about invasiveness, downtime, or visible scarring. This has led to a growing interest in non-invasive or minimally invasive hair transplant methods that offer natural results with minimal discomfort or recovery time.
Understanding Hair Transplant Techniques
To better appreciate the least invasive options available today, it’s essential to understand the two main traditional techniques of hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Both methods involve harvesting hair follicles from a donor area—typically the back or sides of the scalp—and transplanting them to areas affected by hair thinning or baldness.
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp, which makes it more invasive and prone to leaving linear scars. FUE, in contrast, extracts individual hair follicles using a tiny punch device, making it less invasive, though still involving minor surgical tools.
The Shift Toward Minimally Invasive Methods
In recent years, demand has surged for less invasive hair restoration techniques. Innovations in tools and technologies have made it possible to perform procedures with minimal pain, no visible scarring, and shorter downtime. These methods also reduce trauma to the scalp, speeding up hair transplant recovery.
1. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) — A Minimally Invasive Standard
Among existing surgical methods, FUE is widely considered the most non-invasive. Surgeons extract follicular units one by one, typically using a punch device of 0.6–1.0 mm in diameter. No stitches or scalpels are used, and patients often return to normal activities within a few days. This method also avoids the linear scar associated with FUT.
However, despite being less invasive than FUT, FUE still involves small incisions, which may not meet the definition of “non-invasive” for everyone.
2. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) — A Refined FUE Variant
DHI is a modification of the FUE technique. It uses a specialized tool known as the Choi Implanter Pen, which allows both extraction and implantation to be done in one step. This eliminates the need to create incisions or recipient sites beforehand. The entire process is more controlled, allowing for precise placement of grafts and reducing trauma to the scalp.
Patients often report a faster healing process and less post-operative discomfort with DHI compared to traditional FUE.
Introducing Truly Non-Invasive Alternatives
While FUE and DHI are minimally invasive, they still involve minor surgical intervention. For individuals looking for completely non-invasive solutions, the following methods may be of interest. While these do not technically fall under “transplants” in the traditional sense, they represent significant advancements in hair restoration with minimal or no physical intrusion.
3. Stem Cell Hair Restoration
Stem cell therapy involves the extraction of adipose (fat) tissue from the patient’s body, isolating stem cells, and re-injecting them into the scalp. These cells are believed to stimulate hair follicles, improve scalp health, and trigger regrowth in thinning areas.
The process involves no cutting or transplanting of follicles, making it a truly non-invasive approach. While results vary, early studies and clinical trials show promise, especially for early-stage hair loss.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, spinning it in a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the plasma back into the scalp. The growth factors in PRP are thought to stimulate dormant hair follicles and promote natural hair growth.
Though PRP requires needles for injection, it is considered non-surgical and is often used in conjunction with other treatments like FUE for enhanced results.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses red or near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles at a cellular level. This therapy can be delivered via in-clinic laser domes or home-use laser caps. It is FDA-approved for hair loss treatment and is completely non-invasive.
LLLT is most effective for early-stage hair thinning and can help improve hair density and thickness over time with consistent use.
Comparing the Most Non-Invasive Options
Each technique has its pros and cons depending on your individual goals, stage of hair loss, and tolerance for surgical procedures. Below is a summary comparison:
- FUE: Minimally invasive, great for natural results, requires some recovery.
- DHI: Less trauma than FUE, no need for incisions, slightly longer procedure time.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Emerging, regenerative, very low risk, results still under long-term study.
- PRP Therapy: Non-surgical, supportive treatment, good for mild to moderate loss.
- LLLT: Fully non-invasive, gradual improvement, requires ongoing use.
Cost Considerations
The hair transplant cost varies depending on the chosen method, clinic location, number of grafts, and technology used. FUE and DHI tend to be on the higher end due to their labor-intensive nature. PRP and LLLT are more affordable but may require repeated sessions for sustained results. Stem cell therapies, still in the experimental phase in many countries, may not be widely available or covered by insurance.
Expected Results and Realistic Outcomes
While many patients seek fast and dramatic transformations, realistic expectations are key. Non-invasive techniques like PRP, stem cell therapy, and LLLT tend to show gradual improvements over several months. They may not replace traditional transplant results in severe hair loss cases but can be valuable for prevention and density enhancement.
More invasive methods like FUE or DHI yield more immediate and visible changes. Many patients also like to browse hair transplant before and after galleries to assess realistic results and set personal expectations.
Recovery Time and Aftercare
One of the significant advantages of less invasive methods is the faster and smoother recovery period. While FUE and DHI typically require a few days of downtime and special care for the donor and recipient areas, PRP and LLLT involve virtually no recovery. Patients can resume regular activities on the same day in most cases. This makes non-invasive options ideal for busy individuals or those concerned about time off work.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate?
Non-invasive or minimally invasive hair restoration is particularly suited for:
- Individuals in the early stages of hair loss
- Those unwilling to undergo surgical procedures
- People seeking to complement an existing hair transplant
- Patients with health conditions that limit surgical options
However, people with extensive baldness may still need to consider more traditional transplant techniques for satisfactory coverage.
Conclusion
The most non-invasive hair transplant methods available today offer hope to those who are hesitant about surgery but still desire fuller, healthier hair. Techniques such as PRP, stem cell therapy, and LLLT are changing the landscape of hair restoration by offering less downtime, reduced discomfort, and natural results. Among surgical techniques, DHI and FUE continue to lead the way in minimizing invasiveness while delivering long-lasting transformations.
Before deciding on a method, it’s important to consult with a qualified specialist to evaluate your hair loss condition and treatment suitability. Whether you’re seeking a complete transplant or a non-invasive solution for early hair thinning, there is a modern approach to fit your needs and lifestyle.
Related Topics:
- Experimental Hair Loss Therapy Shows Regrowth Promise in Phase 2 Trial
- Hers Launches First Prescription Gummy for Hair Regrowth
- Joel McHale Opens Up About 4 Hair Transplant Surgeries