Platelet – Rich Plasma (PRP) gel has gained popularity in various medical fields, including hair restoration, due to its unique properties that enhance tissue repair and regeneration. Creating PRP gel involves a series of precise steps to ensure the quality and effectiveness of the final product. This article will guide you through the process of making PRP gel, from the necessary materials to the detailed procedures.
Required Materials
Blood Collection Supplies
Sterile Syringes and Needles: You will need several sterile syringes of appropriate sizes, typically 10 – 20 mL, along with corresponding needles. These should be of high quality to ensure a safe and clean blood collection process.
Vacuum Blood Collection Tubes: These tubes are essential for drawing the patient’s blood. They often contain an anticoagulant, such as sodium citrate, to prevent the blood from clotting during collection.
Tourniquet: A tourniquet is used to make the veins more
prominent and easier to access during blood collection. It should be clean and sterile.
Centrifugation Equipment
Centrifuge: A reliable centrifuge capable of spinning at high speeds is crucial. The centrifuge should have adjustable settings for speed and time, as different PRP preparation protocols may require specific centrifugation parameters.
Centrifuge Tubes: Specialized centrifuge tubes that are compatible with the centrifuge machine are needed. These tubes should be able to withstand the forces generated during centrifugation without leaking or breaking.
Additional Materials
Calcium Chloride or Thrombin: These substances are used to initiate the gel – forming process. Calcium chloride is a common choice and helps in the conversion of fibrinogen in the plasma to fibrin, which forms the gel matrix. Thrombin can also be used, as it directly acts on fibrinogen to promote gel formation.
Sterile Mixing Vessels and Pipettes: Sterile containers are required for mixing the components to create the PRP gel. Pipettes are used to accurately measure and transfer the substances during the preparation process.
Sterile Gloves and a Clean Workspace: Maintaining a sterile environment is essential to prevent contamination of the PRP gel. Wearing sterile gloves and working on a clean, disinfected surface helps ensure the safety and efficacy of the gel.
Step – by – Step Procedure
Blood Collection
Patient Preparation: First, prepare the patient for blood collection. Explain the procedure to the patient and ensure they are in a comfortable position. Apply the tourniquet to the patient’s arm to make the veins more visible.
Blood Draw: Using a sterile syringe and needle, carefully draw the required amount of blood, usually around 20 – 60 mL, depending on the intended use of the PRP gel. Transfer the collected blood into the vacuum blood collection tubes containing the anticoagulant.
Centrifugation
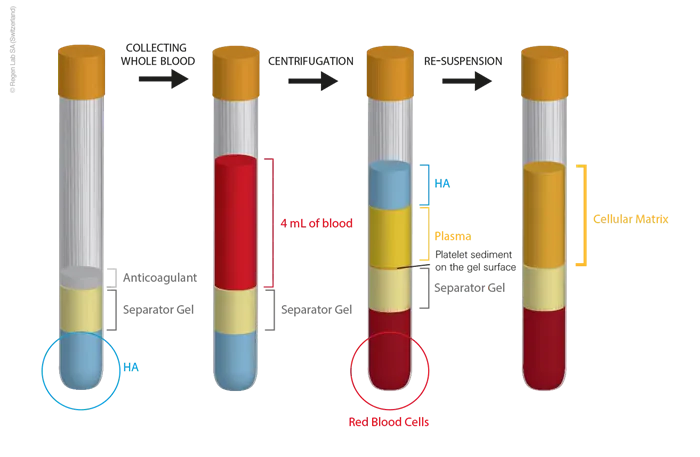
First Spin: Place the blood collection tubes in the centrifuge. Set the centrifuge to a low – speed setting, typically around 1,500 – 2,000 RPM (revolutions per minute), and spin the tubes for 10 – 15 minutes. This first centrifugation separates the blood into three layers: the bottom layer of red blood cells, the middle layer of white blood cells and platelets (the buffy coat), and the top layer of plasma.
Second Spin: Carefully remove the tubes from the centrifuge. Using a pipette, transfer the upper plasma layer, along with the buffy coat, into a clean centrifuge tube. Avoid drawing in any of the red blood cells. Then, set the centrifuge to a higher speed, usually around 3,000 – 3,500 RPM, and spin the tube for another 10 – 15 minutes. This second spin further concentrates the platelets in the plasma, creating the PRP.
Gel Formation
Addition of Gel – Inducing Agent: Once the PRP is obtained, transfer it to a sterile mixing vessel. Add the calcium chloride or thrombin to the PRP according to the recommended concentration. The amount of the gel – inducing agent may vary depending on the volume of the PRP, but a common ratio is around 1 – 2 mL of calcium chloride solution (usually 10% concentration) per 10 mL of PRP.
Mixing: Gently mix the PRP and the gel – inducing agent using a pipette or a sterile stirrer. The mixture will start to thicken and form a gel – like consistency within a few minutes. Ensure thorough mixing to achieve a homogeneous gel.
Quality Control and Safety Considerations
Ensuring Platelet Concentration
It’s important to verify the platelet concentration in the PRP before gel formation. Some clinics may use automated hematology analyzers to measure the platelet count in the PRP. A typical target for PRP used in medical applications is a platelet concentration that is 3 – 5 times higher than the normal blood platelet level. If the platelet concentration is too low, the effectiveness of the PRP gel may be compromised.
Sterility Assurance
Throughout the entire process of making PRP gel, maintaining sterility is of utmost importance. All equipment should be properly sterilized before use, and the procedure should be carried out in a clean environment, preferably in a sterile laminar flow hood if available. Any signs of contamination, such as visible particulate matter in the gel or an unusual odor, should be a cause for discarding the gel and repeating the process.
Storage and Use
Once the PRP gel is made, it should be used as soon as possible. If immediate use is not possible, it can be stored in a sterile container at a cool temperature, preferably between 2 – 8°C. However, prolonged storage may affect the quality and effectiveness of the gel. When using the PRP gel in a medical procedure, such as in hair restoration, ensure that the application is carried out using sterile techniques to prevent any potential infections.
Conclusion
Creating PRP gel is a straightforward process that offers a convenient and effective alternative to traditional PRP injections for hair restoration. By following the steps outlined above, healthcare professionals can produce high-quality PRP gel that delivers sustained release of growth factors to the scalp. PRP gel is a valuable addition to the arsenal of hair restoration treatments, providing patients with a non-invasive option to improve hair density and overall scalp health. As with any medical procedure, it is essential to consult with a qualified specialist to determine the most suitable treatment plan for each individual.
Related topics:
What Are the Three Types of PRP?