Hair transplantation has become a popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss, offering a permanent and effective way to restore hair density and improve one’s appearance. Two of the most widely used techniques in hair restoration are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial for patients to understand the differences to make an informed decision. This article will provide a comprehensive comparison between FUT and FUE, covering their surgical methods, outcomes, recovery times, and costs.
Understanding FUT and FUE
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
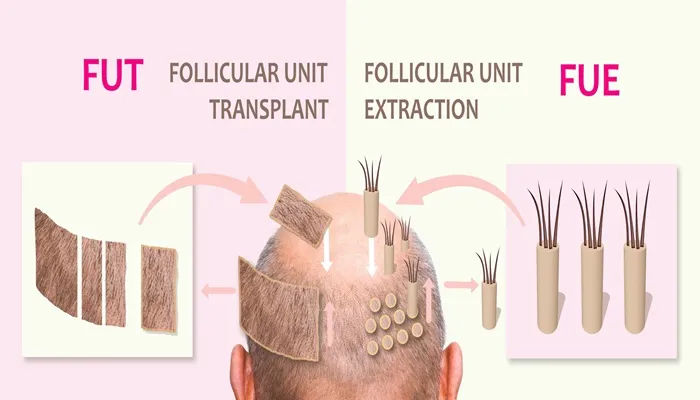
FUT, also known as the strip method, is one of the oldest and most traditional hair transplant techniques. It involves removing a strip of scalp tissue from the donor area, typically the back of the head, and then dissecting this strip into individual follicular units under a microscope. These units, each containing 1-4 hair follicles, are then transplanted into the recipient area where hair loss has occurred.
Advantages of FUT
Higher Yield of Grafts: FUT allows for a large number of grafts to be harvested in a single session, making it suitable for patients with advanced hair loss.
Potentially Higher Graft Survival Rate: Since the follicular units are removed as a strip and then dissected under a microscope, the protective tissue around the follicles is maintained, leading to potentially higher graft survival rates.
Cost-Effective: FUT is generally more affordable compared to FUE, especially for patients who need extensive coverage.
Disadvantages of FUT
Linear Scar: FUT leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which can be visible if the patient opts for short hairstyles.
Longer Recovery Time: The incision made to remove the strip of skin requires sutures and a longer healing period compared to FUE.
Increased Post-Operative Discomfort: FUT is a more invasive procedure, which can result in more discomfort and a longer recovery time.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more modern and minimally invasive technique that involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a micro-punch tool. This method is often preferred for its minimal scarring and shorter recovery time.
Advantages of FUE
Minimally Invasive: FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable compared to the linear scar from FUT.
Shorter Recovery Time: Since there is no large incision, the recovery time is generally shorter, often around a week.
Flexibility in Hairstyling: FUE allows patients to wear their hair short without revealing scars, making it a popular choice for those who prefer short hairstyles.
Disadvantages of FUE
More Time-Consuming: FUE is a more labor-intensive process, as individual follicles are extracted one by one, making it more time-consuming.
Requires Skilled Surgeon: FUE requires a high level of skill and precision from the surgeon to ensure optimal results and minimize damage to the follicles.
Higher Costs: FUE is generally more expensive than FUT due to the increased complexity and time required.
Surgical Methods
FUT Hair Transplant Process
Strip Harvesting: A thin strip of scalp tissue containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area. The length and width of the strip depend on the number of grafts required.
Dissection: The strip is divided into individual follicular units under a microscope, each containing 1-4 hair follicles.
Transplantation: Small incisions are made in the recipient area, and the grafts are carefully placed into these incisions.
FUE Hair Transplant Process
Micro-Punch Extraction: Individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area using a micro-punch tool, typically between 0.7mm to 1mm in diameter.
Sorting and Preservation: The extracted grafts are sorted and preserved in a solution to maximize their survivability.
Implantation: Grafts are individually implanted into the recipient area using an implanter pen (Choi pen) to ensure precise placement.
Aesthetic Outcomes and Results
Scarring
FUT leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which can be concealed with longer hairstyles but may be visible with short hair. In contrast, FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable, making it a preferred choice for patients who like to wear their hair short.
Hair Distribution
FUE offers more flexibility in graft distribution, allowing for a more natural-looking implant pattern that mimics natural hair growth. This can result in a more seamless integration with existing hair compared to FUT.
Graft Survival
FUT generally has a higher graft survival rate due to the intact protective tissue around the follicles during extraction. However, advancements in FUE technology, such as robotic FUE, have improved graft quality and reduced the risk of damage.
Personal Factors and Suitability
Scale of Hair Restoration
FUT is often recommended for patients requiring a large number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for those with extensive hair loss. FUE, while more flexible, may require multiple sessions to achieve the same level of coverage, making it more suitable for those with minimal to moderate hair loss.
Donor Area Density
For patients with limited donor hair density, FUE allows for selective harvesting from various parts of the scalp to prevent visible patchiness. This can be particularly beneficial for those with limited donor hair or those considering body hair transplantation.
Budget
FUT is generally more cost-effective, with average costs ranging from $5,000 to $12,000. FUE, due to its labor-intensive nature, is typically more expensive, with costs ranging from $6,000 to $15,000.
Recovery and Downtime
FUT has a longer recovery period, typically around 2 weeks, with moderate swelling following surgery. FUE, being less invasive, has a shorter recovery time of about a week.
Conclusion
Both FUT and FUE are effective hair transplant techniques, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. FUT is ideal for patients requiring a large number of grafts and those who do not mind a linear scar in the donor area. FUE, on the other hand, offers minimal scarring, shorter recovery times, and greater flexibility in hairstyling, making it a popular choice for many patients.
Ultimately, the choice between FUT and FUE depends on individual needs, preferences, and the specific recommendations of your hair restoration specialist. Consulting with a qualified professional can help you determine the best option for your unique situation, ensuring optimal results and a satisfactory recovery experience.
Related topics:
- FUE vs. FUT Hair Transplant: Understanding Your Options
- FUE vs FUT Success Rate: Which is Better?
- FUE vs. FUT Hair Transplant: A Comprehensive Comparison