The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and various bodily functions. It produces hormones—triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)—that control metabolism, energy production, and the functioning of organs and tissues throughout the body. When the thyroid gland malfunctions, it can lead to various health issues, including hair loss.
Connection Between Thyroid and Hair Loss
Thyroid conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can disrupt the normal functioning of the hair growth cycle, resulting in hair loss. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones, leading to a slowdown in metabolism and a decrease in cellular activity, including the growth of hair follicles. Conversely, in hyperthyroidism, excessive thyroid hormone production can accelerate metabolic processes, causing hair follicles to enter the resting phase prematurely, leading to hair loss.
Specific Thyroid Conditions Causing Hair Loss
Two primary thyroid conditions, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, are closely associated with hair loss. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing inflammation and eventual destruction of thyroid tissue. As thyroid function declines, symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss may manifest. On the other hand, Graves’ disease, another autoimmune disorder, results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and hair thinning.
Symptoms of Thyroid-Related Hair Loss
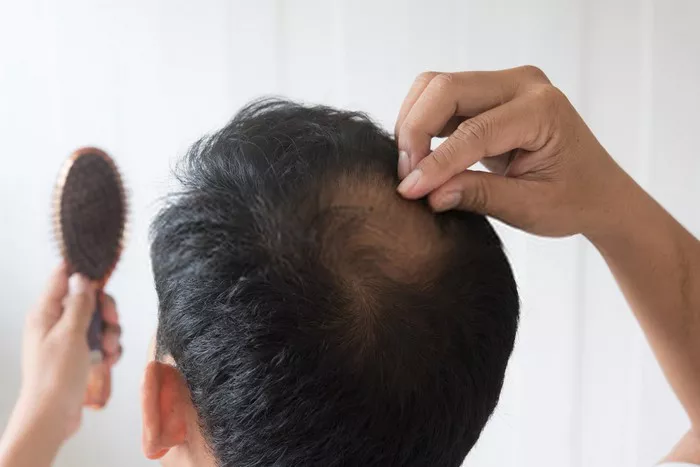
Thyroid-related hair loss typically presents as diffuse thinning across the scalp, rather than localized bald patches. Individuals may notice increased shedding during routine activities such as washing or brushing hair. In addition to scalp hair loss, eyebrows may also become sparse, and body hair may thin out. Other symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, such as fatigue, weight changes, and changes in mood, may accompany hair loss.
Treatment Options
Treatment for thyroid-related hair loss focuses on addressing the underlying thyroid condition to restore hormonal balance and promote hair regrowth. In cases of hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormones such as levothyroxine is the primary treatment. Conversely, hyperthyroidism may be managed with medications that suppress thyroid hormone production or radioactive iodine therapy to reduce thyroid function. Alongside medical interventions, lifestyle modifications such as stress management, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep can support overall health and hair growth.
Prevention Tips
While some factors contributing to thyroid dysfunction, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, certain lifestyle choices may help prevent or minimize hair loss associated with thyroid conditions. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients such as iodine, selenium, zinc, and iron supports thyroid function and hair health. Additionally, managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can help mitigate the impact of stress-related hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized recommendations for dietary modifications and supplements to support thyroid function and hair growth.
When to See a Doctor
It is essential to seek medical evaluation if experiencing symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, including unexplained hair loss, fatigue, weight changes, or changes in mood or energy levels. A healthcare provider can perform blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels and thyroid antibody levels, aiding in the diagnosis of thyroid conditions such as hypothyroidism or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Early detection and management of thyroid disorders can help prevent complications and promote overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, thyroid conditions can significantly impact hair health and contribute to hair loss through disruptions in the hair growth cycle. Understanding the connection between thyroid function and hair loss, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical evaluation and treatment are essential steps in managing thyroid-related hair loss effectively. By addressing underlying thyroid issues and adopting lifestyle modifications to support thyroid function, individuals can promote hair regrowth and maintain overall health and vitality.
FAQs
1. How serious is Hashimoto’s disease?
Hashimoto’s disease, also known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, is a chronic autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. It can lead to inflammation and damage to the thyroid, causing hypothyroidism. While Hashimoto’s itself isn’t usually life-threatening, if left untreated, it can cause complications such as heart problems, infertility, and mental health issues. However, with proper management, including medication and lifestyle changes, many people with Hashimoto’s can lead normal, healthy lives.
2. How to know if your thyroid is off?
Symptoms of thyroid imbalance can vary depending on whether it’s underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism). Common signs of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, and feeling cold. On the other hand, symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and heat intolerance. If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis through blood tests and physical examination.
3. How to fix thyroid imbalance?
Treatment for thyroid imbalance depends on the specific condition and its severity. For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone medication is typically prescribed to replace the hormone your thyroid isn’t producing enough of. For hyperthyroidism, treatment may involve medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery in severe cases. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and regular exercise can support thyroid health and overall well-being.
4. What does thyroid hair loss look like?
Thyroid-related hair loss can present as thinning hair, especially at the crown of the head, and a widening part. Unlike typical male or female pattern baldness, which often affects specific areas, thyroid-related hair loss tends to be more diffuse. You may also notice changes in the texture of your hair, such as dryness or brittleness. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing hair loss, as it can be a symptom of various health conditions, including thyroid issues. Treatment for thyroid-related hair loss typically involves addressing the underlying thyroid imbalance through medication and lifestyle adjustments.