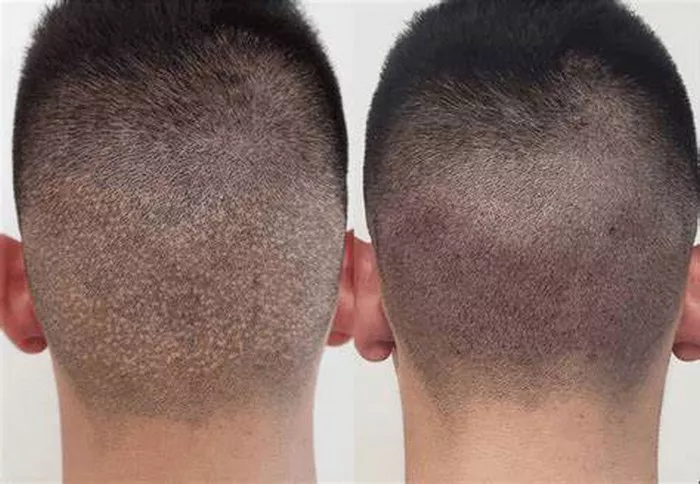
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) has revolutionized the way hair restoration is performed, offering a minimally invasive option for those suffering from hair loss. After undergoing hair transplant surgery, many patients experience a natural phase where the newly transplanted hair begins to shed. This shedding stage often raises concerns and questions: When does hair shed after FUE? Is it normal? How long does it last? And what should patients expect during this critical recovery phase?
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the timeline of hair shedding post-FUE, the biological reasons behind it, and essential information to help patients understand and manage their hair transplant recovery journey effectively.
Understanding FUE Hair Transplantation
Before diving into the shedding timeline, it’s important to understand what FUE entails. Unlike the traditional strip method, FUE involves harvesting individual hair follicles from the donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and implanting them into the thinning or bald areas. This technique is praised for leaving minimal scarring and a quicker healing time.
What Happens After an FUE Procedure?
Immediately following the procedure, the scalp may exhibit redness, minor swelling, and scabbing around the implanted follicles. The transplanted hairs typically remain visible initially, giving patients the impression that new hair growth has already started. However, this is just the beginning of a complex biological process.
When Does Hair Shed After FUE?
The shedding phase, medically referred to as “shock loss,” usually begins around 2 to 4 weeks after the FUE procedure. This is a normal and expected part of the hair transplant cycle. During this time, the transplanted hair shafts fall out, but the hair follicles themselves remain intact beneath the skin.
This shedding is caused by the trauma the follicles experience during transplantation, which temporarily pushes them into a resting phase (telogen phase) before new hair growth can begin. It’s important to emphasize that shedding does not mean the transplant has failed; rather, it is an essential step toward healthy, long-lasting hair growth.
Detailed Timeline of Hair Shedding and Growth After FUE
First Week: Immediate Post-Op Phase
During the first week, the grafts settle into their new positions. Mild swelling and scabbing are common, and patients should follow their surgeon’s post-operative care instructions carefully to avoid infection or graft dislodgement.
Weeks 2 to 4: Shedding Phase Begins
Between 2 to 4 weeks post-operation, the transplanted hair shafts start to shed. This is often the most worrying period for patients because visible hair loss may seem alarming. However, the follicles beneath the scalp remain healthy and ready to produce new hair.
Months 1 to 3: Dormant Phase
After shedding, the hair follicles enter a resting phase lasting around 1 to 3 months. No visible hair growth occurs during this time, which can be frustrating for patients eager to see results.
Months 3 to 6: Initial New Hair Growth
New hair begins to emerge around the 3rd month. These hairs may be thin and fine initially but will thicken over time. This marks the end of the shedding phase and the beginning of sustained growth.
Months 6 to 12: Continued Hair Growth and Maturation
Hair density and thickness improve significantly during this period. Most patients notice noticeable improvements in hair volume and coverage by the end of the first year.
Why Does Hair Shedding Occur After FUE?
The shedding phase after a hair transplant is primarily due to the natural hair cycle disruption caused by the transplantation trauma. Hair follicles cycle through three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). The FUE procedure temporarily pushes follicles into the telogen phase, causing hair shafts to shed before new growth begins.
This process is essential because it clears the way for fresh, healthy hair to grow from the transplanted follicles. Without this shedding phase, the new follicles wouldn’t properly establish themselves, which could compromise the transplant results.
How to Care for Your Hair After FUE to Minimize Shedding Concerns
Understanding the shedding timeline can help patients manage expectations, but proper post-operative care is equally important. Here are some essential tips:
- Follow Surgeon’s Instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific care protocols for washing, avoiding direct sun exposure, and refraining from strenuous activities that may disrupt healing.
- Gentle Hair Washing: Use mild shampoos and avoid vigorous rubbing in the first few weeks to protect the grafts.
- Avoid Touching or Scratching: Scabs and crusts protect the transplanted follicles; disturbing them can cause graft loss.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Nutrients like vitamins A, C, D, E, biotin, and zinc support hair follicle health and regeneration.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both can impair blood flow and slow down the recovery process.
When Should You Be Concerned About Hair Shedding?
While shedding after an FUE hair transplant is normal, excessive shedding or hair loss from the donor or non-transplanted areas may require medical evaluation. Consult your hair transplant specialist if you experience:
- Persistent redness or swelling beyond the initial recovery period
- Signs of infection, such as pus or severe pain
- Sudden and severe shedding outside the typical 2-4 week window
- Hair loss in the donor area that seems unusual
What to Expect Long-Term
By understanding the typical hair transplant recovery process, including when hair sheds after FUE, patients can feel more confident about their journey. Transplanted hair is generally permanent, as the follicles taken from the donor site are resistant to the hormone responsible for male pattern baldness.
Most patients achieve full results between 9 and 12 months, with some continuing to see improvements up to 18 months post-procedure. Patience and proper care are critical to achieving the best possible outcome.
Conclusion
Hair shedding after FUE is a natural, expected part of the post-operative process and typically begins 2 to 4 weeks after surgery. This phase, although sometimes unsettling for patients, is essential for the new follicles to settle and begin producing healthy hair. Understanding the timeline and reasons behind shedding helps reduce anxiety and promotes a better recovery experience.
If you are considering a hair transplant, it’s vital to research both the procedure and the hair transplant cost and recovery expectations beforehand to make an informed decision. Consulting with a qualified specialist will ensure personalized care and guidance throughout your hair restoration journey.
Related Topics:
- Hair Transplant Safety Tips: What to Check Before Surgery
- Top 8 Hair Transplant Surgeons to Know in 2025
- When Does Hair Stop Receding? | A Complete Guide